Are Air Source Heat Pump Suitable for Old Building?
Air source heat pumps are designed with modern homes in mind. Because of the design differences between a modern home and an older home, it's good to know if an air source heat pump works in older homes as well.
The main issues to consider when installing an air source heat pump in an older house are how the heat is dissipated (is your radiator, floor heating or other heat radiator suitable) and whether the house can hold the heat generated (is the insulation suitable).
Due to the technical differences in the structural design of modern and older homes, renovations have to be carried out on older homes to take full advantage of the capabilities of these heat pumps.
How does an air source heat pump work?
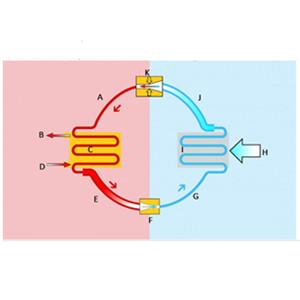
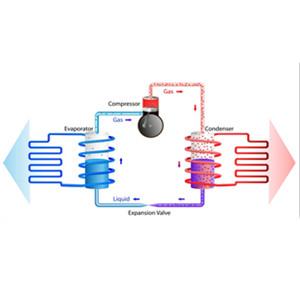
Typically, an air source heat pump has an outdoor unit and an indoor air handling unit. The outer unit has tubes filled with liquid refrigerant. When outside air blows through the tubes, the refrigerant heats up and turns into a gas.
The gas then passes through a compressor, further raising its temperature. Heat exchangers transfer heat to heat radiators, such as radiators or underfloor heating systems. At the same time, the refrigerant becomes liquid again and the process continues.
Different types of heat pumps
The three different types of heat pumps have different requirements.
* air to water
* brine
* water to water

Air-to-Water Heat Pumps (Air Source Heat Pumps)
Air source heat pumps draw heat from the surrounding air and use it for heating purposes. This type of heat pump is generally less efficient than other types, but is the easiest to install.
Efficient, environmentally friendly, eligible for funding: Heat pumps are not only efficient and environmentally friendly, they are also very quiet. It also uses natural coolant. On top of that, particularly high subsidies are available when installing these heat pumps in older buildings.
Brine heat pump (geothermal heat pump)
This type of heat pump uses geothermal heat as a heat source. They come in two designs:
with horizontal collector or
With vertical drilling.
Horizontal collectors are installed below the surface. Compared to vertical drilling, they do not require any deep drilling work but take up a larger area. Geothermal heat pumps have excellent levels of efficiency because the ground retains heat even in winter.
Water to water heat pump (water source heat pump)
Water source heat pumps draw heat from groundwater, for which two wells must be drilled. They have the highest level of efficiency because the temperature of the groundwater is always above 0°C.
The difference between coolant temperature and flow temperature is also lower than other heat pumps. However, you will need a permit to drill wells in most areas.
How economical are heat pumps in older buildings?
The smaller the difference between the ambient temperature and the flow temperature of the heating system, the more efficiently the heat pump will work.
Flow temperature describes the temperature of the hot water supplied to the floor heating or radiator. The temperature of the heated water is mostly measured directly after it comes out of the heat generator.
The problems faced by heat pumps in older buildings are
1. The temperature of the air, groundwater or ground is very low, especially in winter.
2. At the same time, the flow temperature of the heating system in old buildings is usually high because the radiators are relatively small, and the thermal insulation of old buildings is usually poor.
The heating system consumes more electricity to compensate for this temperature difference. Still, heat pumps can work efficiently in older buildings. Because of how they work, heat pumps can generate four to five times more thermal energy than is consumed using electricity.
When is it worthwhile to equip an older building with a heat pump?
Was your house built before 1970? If your home's energy efficiency has not been upgraded since then, replacing the heating system in an older building may be beneficial. Older gas and oil heating systems without condensing technology should definitely be replaced with modern equipment.
To calculate whether using a heat pump in an older building makes economic sense and whether it will get the right funding, you need to understand the seasonal performance factor, or SPF for short. This value tells you how many units of heat the heat pump produces from one unit of electricity.
SPF = Thermal Energy (kWh/year) / Electricity (kWh/year)
Heat pumps are more economical than oil heating systems if the SPF is greater than 1.7. To be more efficient than gas heating systems, heat pumps must have an SPF greater than 2.5. Heat pumps with these SPF values are also more environmentally friendly than gas or oil heating systems.
In practice, however, the seasonal performance factor must be higher than the sample value calculated using fuel prices. After all, the purpose is to recoup the higher purchase price of the heat pump. Maintenance costs are also incurred.
Typical SPF values for various heat pump types are as follows:
Air to water heat pump: 2.9 (some even 4-5)
Brine heat pump: 3.9
Water-to-Water Heat Pumps: 5
Air to water heat pump
LMA-monomer
The WOLF LMA Integral Heat Pump is sure to fit the overall design of your home and is perfect for garden, patio or wall mounting - all with an impressive COP of 4.65.
How to Improve the Efficiency of Heat Pumps in Old Buildings
As mentioned earlier, the better the insulation of an older building, the more worthwhile it is to install a heat pump. Then you'll use less electricity to heat your home. If you want to upgrade your insulation, you should improve cellar ceilings and attic floors. You can also replace windows and add insulation to the facade, but these measures are more expensive.
You can also significantly reduce flow temperatures by replacing old radiators with radiant panels or underfloor heating systems. This makes the heat pump more efficient. Let an expert make adjustments and regular repairs to your entire heating system. A heating system that is not set up correctly can waste energy.
Heat Pump Subsidy for Old Buildings
Energy suppliers, municipal utilities and federal states also offer subsidies. Our free subsidy information service gives you a quick and easy overview of all possible funding schemes.
In conclusion
Heat pumps in everyday use and possible alternatives
Using heat pumps in older buildings is environmentally friendly and under certain conditions makes economic sense, especially given the many financing opportunities. So find out these before moving on.
Alternatively, you can combine a heat pump with a gas heating system or choose a modern gas condensing boiler as the only heat generator.